OVERVIEW
In my previous blog posts, we got to know what Jenkins is and its importance as a continuous integration tool. In this article, we will be going through how to work with Jenkins on an Ubuntu operating system. Let's get right into it.
Quickstart
Step 1:- Install Jenkins and its dependencies
Update the server and install JDK since Jenkins is a Java-based application
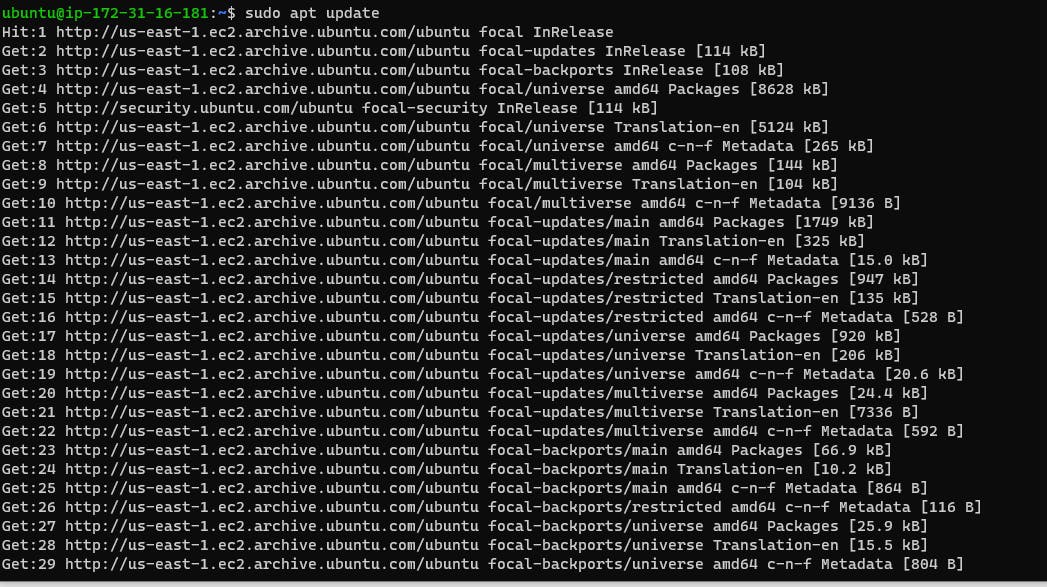
sudo apt update
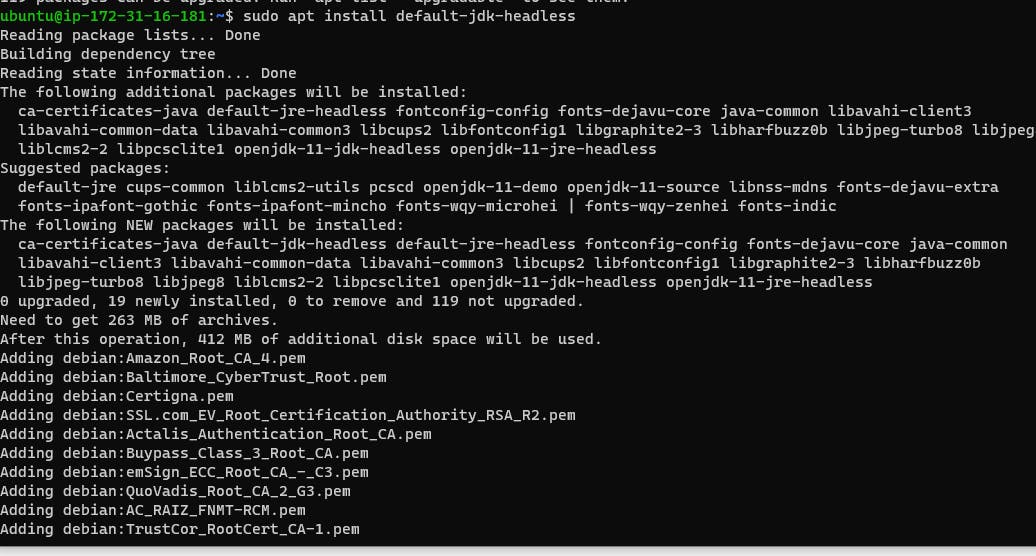
sudo apt install default-jdk-headless
Install Jenkins and ensure that it is running
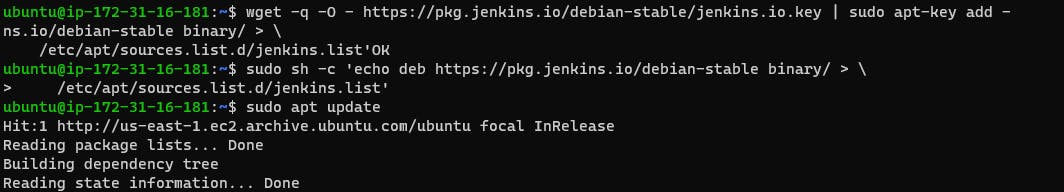
wget -q -O - https://pkg.jenkins.io/debian-stable/jenkins.io.key | sudo apt-key add -
sudo sh -c 'echo deb https://pkg.jenkins.io/debian-stable binary/ > \
/etc/apt/sources.list.d/jenkins.list'
sudo apt update
sudo apt-get install jenkins
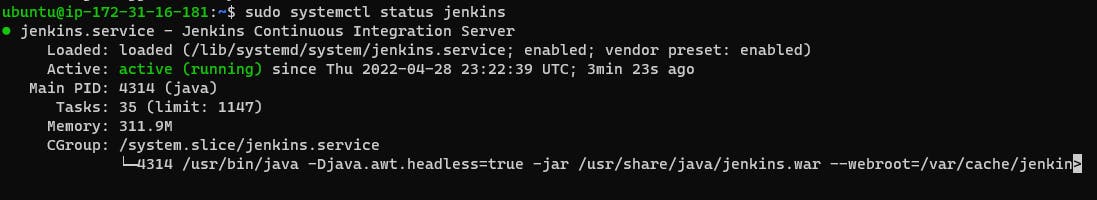
sudo systemctl status jenkins
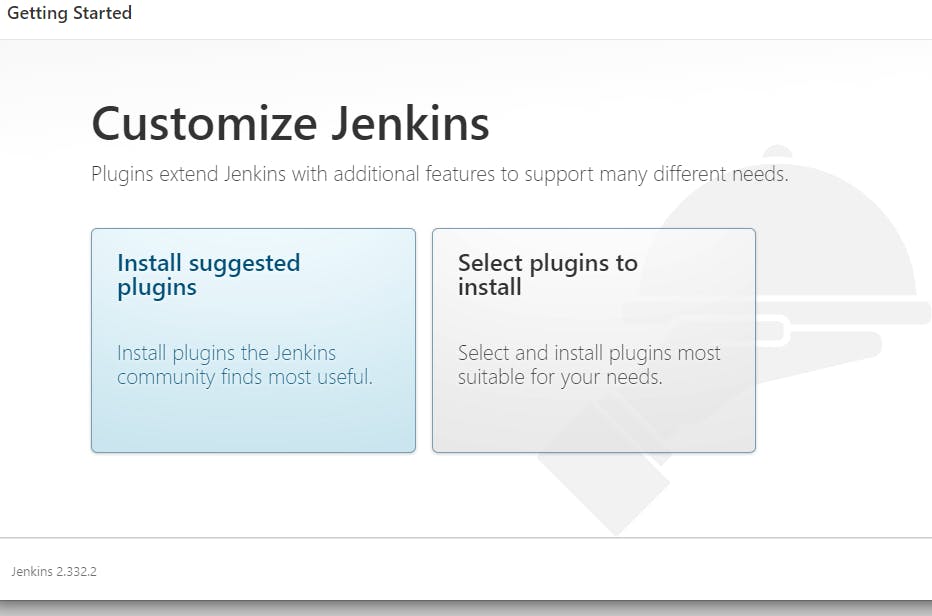
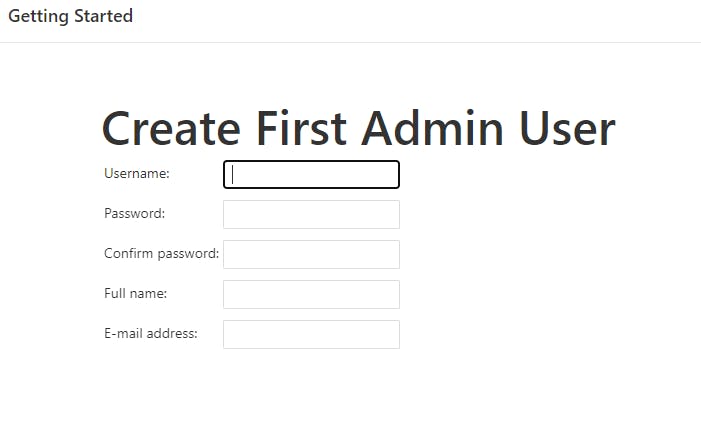
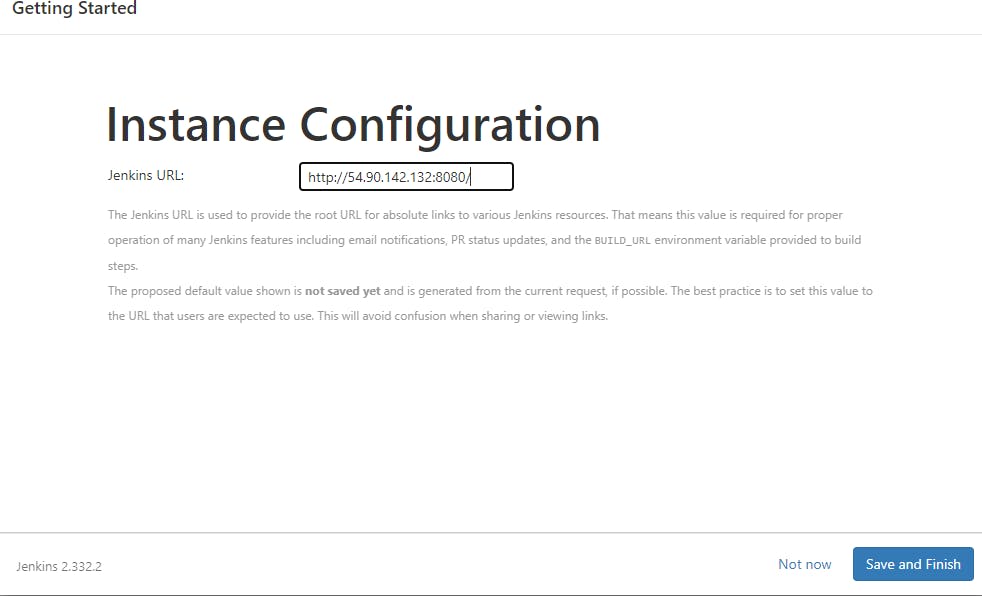
Step 2:- Perform Initial Jenkins setup
Access the public IP address of your Jenkins server from your web browser
http://<Jenkins-Server-Public-IP-Address-or-Public-DNS-Name>:8080
To ensure Jenkins is securely set up by the administrator, a password has been written in a file on the server but you have to check the file, copy the password and paste it on the Jenkins console before you can continue the Jenkins setup.
Just run `sudo cat /var/lib/jenkins/secrets/initialAdminPassword` on the terminal you're using and get
the password.